Futurama
| Futurama | |
|---|---|
| Genre | Sitcom Animation Science fiction |
| Format | Animated series |
| Created by | Matt Groening |
| Developed by | Matt Groening David X. Cohen |
| Voices of | Billy West Katey Sagal John DiMaggio Tress MacNeille Maurice LaMarche Lauren Tom Phil LaMarr David Herman |
| Theme music composer | Christopher Tyng |
| Opening theme | "Theme from Futurama" |
| Composer(s) | Christopher Tyng |
| Country of origin | United States |
| Language(s) | English |
| No. of seasons | 6 |
| No. of episodes | 114 (List of episodes) |
| Production | |
| Executive producer(s) | Matt Groening David X. Cohen Ken Keeler co-executive producers: Patric M. Verrone Josh Weinstein Eric Horsted Michael Rowe Dan Vebber |
| Producer(s) | Lee Supercinski Claudia Katz |
| Running time | 22 minutes |
| Production company(s) | The Curiosity Company 20th Century Fox Television |
| Distributor | 20th Television |
| Broadcast | |
| Original channel | Fox (1999–2003) Comedy Central (2008–present) |
| Picture format | 480i (4:3 SDTV) (season 1–4) 1080i (16:9 HDTV) (season 5–) |
| Audio format | Dolby Surround (season 1–4) Dolby Digital 5.1 (season 5–) |
| Original run | March 28, 1999 – August 10, 2003; March 23, 2008 – present |
| External links | |
| Website | |
Futurama is an American animated science fiction sitcom created by Matt Groening and developed by Groening and David X. Cohen for the Fox Broadcasting Company. The series follows the adventures of a late 20th-century New York City pizza delivery boy, Philip J. Fry, who, after being unwittingly cryogenically frozen for one thousand years, finds employment at Planet Express, an interplanetary delivery company in the retro-futuristic 31st century. The series was envisioned by Groening in the late 1990s while working on The Simpsons, later bringing Cohen aboard to develop storylines and characters to pitch the show to Fox.
In the United States, the series aired on Fox from March 28, 1999 to August 10, 2003 before ceasing production. Futurama was then aired in reruns on Cartoon Network's Adult Swim from January 1, 2003 to December 31, 2007, until the network's contract expired. It was revived in 2007 as four straight-to-DVD films; the last of the four was released in early 2009. Comedy Central entered into an agreement with 20th Century Fox Television to syndicate the existing episodes and air the films as 16 new, half-hour episodes.[1][2]
Comedy Central began airing Futurama on January 2, 2008, with new episodes starting on March 23, 2008.[3] In June 2009, producing studio 20th Century Fox announced that Comedy Central had picked up the show for 26 new half-hour episodes, of which the first half began airing from June 24, 2010. The remaining thirteen episodes began airing on June 23, 2011.[4] In March 2011, it was announced that Futurama has been renewed for a seventh season, consisting of at least 26 episodes, scheduled to air in 2012 and 2013.[5][6]
Throughout its run, Futurama has consistently received high critical acclaim, culminating in a Guinness World Record for "Current Most Critically Acclaimed Animated Series" in 2010.[7][8] Futurama has also been nominated for 17 Annie Awards and 10 Emmy Awards, winning seven and five, respectively. Futurama has also been nominated four times for a Writers Guild of America Award, winning two for the episodes "Godfellas" and "The Prisoner of Benda", and nominated for a Nebula Award. The show also received an Environmental Media Award for "The Problem With Popplers".
Futurama-related merchandise has also been released, including: a tie-in comic book series and video game, calendars, clothes, and figurines.
Contents |
Origins
Fox expressed a strong desire in the mid-1990s for Matt Groening to create a new series, and he began conceiving Futurama during this period. In 1996, he enlisted David X. Cohen, then a writer and producer for The Simpsons, to assist in developing the show. The two spent time researching science fiction books, television shows, and films. When they pitched the series to Fox in April 1998, Groening and Cohen had composed many characters and story lines; Groening claimed they had gone "overboard" in their discussions.[9] Groening described trying to get the show on the air as "by far the worst experience of [his] grown-up life."[10] During that first meeting, Fox ordered thirteen episodes. Immediately after, however, Fox feared the themes of show were not suitable for the network and Groening and Fox executives argued over whether the network would have any creative input into the show.[11] With The Simpsons the network has no input.[12] Groening explains, "When they tried to give me notes on Futurama, I just said: 'No, we're going to do this just the way we did Simpsons.' And they said, 'Well, we don't do business that way anymore.' And I said, 'Oh, well, that's the only way I do business.'"[13] After negotiations, he received the same independence with Futurama.
The name Futurama comes from a pavilion at the 1939 New York World's Fair. Designed by Norman Bel Geddes, the Futurama pavilion depicted how he imagined the world would look in 1959.[14] Many other titles were considered for the series, including "Aloha, Mars!" and "Doomsville", which Groening notes were "resoundly rejected, by everyone concerned with it".[15][16]
Production
It takes approximately six to nine months to produce an episode of Futurama.[17][18] The long production time results in several episodes being worked on simultaneously.[19]
Executive producers
Matt Groening and David X. Cohen have served as executive producers and show runners during the show's entire run, and also function as creative consultants. Ken Keeler became an executive producer for Season 4 and subsequent seasons.
Writing
The planning for each episode begins with a table meeting of writers, who discuss the plot ideas as a group. A single staff writer writes an outline and then produces a script. Once the first draft of a script is finished, the writers and executive producers call in the actors to do a table read.[11] After this script reading, the writers collaborate to rewrite the script as a group before eventually sending it to the animation team.[20] At this point the voice recording is also started and the script is out of the writers' hands.[18]
Voice actors
Futurama has eight main cast members. Billy West performs the voices of Philip J. Fry, Professor Farnsworth, Doctor Zoidberg, Zapp Brannigan and many other incidental characters. West auditioned for "just about every part", landing the roles of the Professor and Doctor Zoidberg.[21] Although West read for Fry, his friend Charlie Schlatter was given the role of Fry.[21] Due to a casting change, West was called back to audition again and was promptly awarded the role. West claims that the voice of Fry is deliberately modeled on his own, so as to make it difficult for another person to replicate the voice.[21] Doctor Zoidberg's voice is based on Lou Jacobi and George Jessel.[22] The character of Zapp Brannigan was originally created and intended to be performed by Phil Hartman.[21][22] Hartman insisted on auditioning for the role, and "just nailed it" according to Matt Groening. Due to Hartman's death, West was subsequently given the role. West states that his version of Zapp Brannigan is an imitation of Hartman and also "modeled after a couple of big dumb announcers I knew."[21][22]
Katey Sagal voices exclusively Leela, and is the only member of the main cast to voice only one character. The role of Leela was originally assigned to Nicole Sullivan.[21] Due to a casting change, Sagal was later given the role of Leela. In an interview in June 2010, Sagal remarked that she did not know that another person was to originally voice Leela until many years after the show first began; going on to state that she is still unaware who the original voice actor even is.[23]
John DiMaggio performs the voice of the robot Bender Bending Rodríguez and other, more minor, characters. Bender was the most difficult character to cast, as the show's creators had not decided what a robot should sound like.[24] DiMaggio originally auditioned for the role of Professor Farnsworth, using the voice he uses to perform Bender, and also auditioned for Bender using a different voice.[25] DiMaggio describes Bender's voice as a combination of a sloppy drunk, Slim Pickens and a character his college friend created named "Charlie the sausage-lover".[23]
Tress MacNeille voices Mom and various other characters. Maurice LaMarche voices Kif Kroker and several supporting characters. Lauren Tom voices Amy Wong, and Phil LaMarr voices Hermes Conrad. David Herman voices Scruffy and various supporting characters. During seasons 1-4, LaMarche is billed as supporting cast and Tom, LaMarr and Herman billed as guest stars, despite appearing in most episodes. LaMarche is promoted to main cast and Tom, LaMarr and Herman to supporting cast in Season 5, and promoted again to main cast in Season 6.
| Main cast members | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Billy West | Katey Sagal | John DiMaggio | Tress MacNeille | Maurice LaMarche | Lauren Tom | Phil LaMarr | David Herman |
| Philip Fry, Professor Farnsworth, Doctor Zoidberg, Zapp Brannigan, various | Leela | Bender, various | Mom, various | Kif Kroker, various | Amy Wong, various | Hermes Conrad, various | Scruffy, various |
In addition to the main cast, Frank Welker, who voices Nibbler, Kath Soucie and Danny Jacobs voice supporting and minor characters. Like The Simpsons, many episodes of Futurama feature guest voices from a wide range of professions, including actors, entertainers, bands, musicians and scientists. Many guests stars voice supporting characters, although many voice themselves; usually as their own head preserved in a jar. Recurring guest stars include Dawnn Lewis, Tom Kenny, Phil Hendrie, Dan Castellaneta, Coolio, Al Gore and Stephen Hawking, among others.
Animation
Rough Draft Studios animates Futurama. The studio receives the completed script of an episode and storyboard it into over 100 drawings. They then create a pencil-drawn animatic with 1000 frames. Rough Draft's sister studio in South Korea renders the 30,000-frame finished episode.[11]
In addition to traditional cartoon drawing, Rough Draft Studios often uses CGI for fast or complex shots, such as the movement of spaceships, explosions, nebula, and snow scenes. The opening sequence is entirely rendered in CGI. The CGI is rendered at 24 frames per second (as opposed to hand-drawn often done at 12 frames per second) and the lack of artifacts makes the animation appear very smooth and fluid. CGI characters look slightly different due to spatially "cheating" hand-drawn characters by drawing slightly out of proportion or off-perspective features to emphasize traits of the face or body, improving legibility of an expression. PowerAnimator is used to draw the comic-like CGI.[26]
The series began high-definition production in Season 5, with Bender's Big Score. The opening sequence was re-rendered and scaled to adapt to the show's transition to 16:9 widescreen format.
For the final episode of Season 6, Futurama is completely reanimated in three different styles: the first segment of the episode features black-and-white Fleischer and Walter Lantz style animation, the second is drawn in the style of a low-resolution video game, and the final segment is in the style of Japanese anime.[27]
Cancellation and revival
Groening and Cohen wanted Futurama to be shown at 8:30 on Sunday nights, following The Simpsons. The Fox network disagreed, opting instead to show two episodes in the Sunday night lineup before moving the show to a regular time slot on Tuesday.[28] Beginning with its second broadcast season Futurama was again placed in the 8:30 Sunday spot,[29] but by mid-season the show was moved again, this time to 7:00 p.m. on Sunday, its third position in under a year.[30]
Even by the fourth season Futurama was still being aired erratically.[31] This was parodied in the opening sequence of the last episode of Season 4 with a picture of Fry, Leela, and Bender captioned "See You On Some Other Channel." Due to being regularly pre-empted by sporting events, it became difficult to predict when new episodes would air. This erratic schedule resulted in Fox not airing several episodes that had been produced for seasons three and four, instead holding them over for a fifth broadcast season. Fox executives were also not supporters of the show.[32] Although Futurama was never officially cancelled, midway through the production of the fourth season, Fox decided to stop buying episodes of Futurama, letting it go out of production before the fall 2003 lineup.[33][34]
In 2005, Comedy Central acquired the syndication rights to Futurama.[35] During the negotiations, Comedy Central discussed the possibility of producing new episodes. In 2006, it was announced that four straight-to-DVD films would be produced, and later split into 16 episodes comprising a new season.[36]
Since no new Futurama projects were in production at the time of release, the final movie release Into the Wild Green Yonder was designed to stand as the Futurama series finale. However, Groening had expressed a desire to continue the franchise in some form, including as a theatrical film.[37] In an interview with CNN, Groening said that "we have a great relationship with Comedy Central and we would love to do more episodes for them, but I don't know... We're having discussions and there is some enthusiasm but I can't tell if it's just me."[38]
On June 9, 2009, 20th Century Fox announced that Comedy Central had picked up the show for 26 new half-hour episodes that began airing on June 24, 2010.[39][40][41] The returning writing crew was smaller than the original crew.[42] It was originally announced that main voice actors West, DiMaggio, and Sagal would return as well, but on July 17, 2009, it was announced that a casting notice was posted to replace the entire cast when 20th Century Fox Television would not meet their salary demands.[43] The situation was later resolved, and the entire original voice-cast returned for the new episodes. The dispute had stopped the original actors from appearing on the Futurama panel for Comic-Con 2009, to the disappointment of fans.[44]
Near the end of a message from Maurice LaMarche sent to members of the "Save the Voices of Futurama" group on Facebook, LaMarche announced that the original cast would be returning for the new episodes.[45] The Toronto Star confirmed, announcing on their website that the original cast of Futurama signed contracts with Fox to return for 26 more episodes.[46] Similarly, an email sent to fans from Cohen and Groening reported that West, Sagal, DiMaggio, LaMarche, MacNeille, Tom, LaMarr, and Herman would all be returning for the revival.[47]
Cohen told Newsday in August 2009 that the reported 26-episode order means "[i]t will be up to 26. I can't guarantee it will be 26. But I think there's a pretty good chance it'll be exactly 26. Fox has been a little bit cagey about it, even internally. But nobody's too concerned. We're plunging ahead".[48] Two episodes were in the process of being voice-recorded at that time, with an additional "six scripts ... in the works, ranging in scale from 'it's a crazy idea that someone's grandmother thought of' to 'it's all on paper'.[48]
When Futurama aired June 24, 2010, on Comedy Central, it helped the network to its highest-rated night in 2010 and its highest-rated Thursday primetime in the network's history.[49] The show has since been renewed for a seventh season, consisting of at least 26 episodes, scheduled to air in 2012 and 2013.[5]
In July 2011, it was reported that the show has been picked up for syndication by both CW affiliates and WGN America. Broadcast of old episodes began in September 2011.[50]
On September 19, 2011, WGN America began re-running Futurama, and now airs the series weeknights at 1:30a ET and 2a ET, and on Saturday nights at 3:30a ET.[51]
Characters
Futurama is essentially a workplace sitcom, the plot of which revolves around the Planet Express interplanetary delivery company and its employees,[52] a small group that largely fails to conform to future society.[53] Episodes usually feature the central trio of Fry, Leela, and Bender, though storylines centered on the other main characters are common.
- Philip J. Fry (Billy West)
- Fry is a dim-witted, immature, slovenly, yet good-hearted pizza delivery boy who falls into a cryogenic pod, causing it to activate and freeze him just after midnight on January 1, 2000. He re-awakens on New Year's Eve, 2999, and gets a job as a cargo delivery boy at Planet Express, a company owned by his only living relative, Professor Hubert J. Farnsworth. Fry's love for Leela is a recurring theme throughout the series.
- Turanga Leela (Katey Sagal)
- Leela is the competent, one-eyed captain of the Planet Express Ship.[52] Abandoned as a baby, she grew up in the Cookieville Minimum Security Orphanarium believing herself to be an alien from another planet, but learns that she is actually a mutant from the sewers in the episode "Leela's Homeworld".[54] Prior to becoming the ship's captain, Leela worked as a career assignment officer at the cryogenics lab where she first met Fry. She is Fry's primary love interest. Her name is a reference to the Turangalîla-Symphonie by Olivier Messiaen.[55]
- Bender Bending Rodríguez (John DiMaggio)
- Bender is a foul-mouthed, heavy-drinking, cigar-smoking, kleptomaniacal, misanthropic, egocentric, ill-tempered robot manufactured by Mom's Friendly Robot Company. He was originally programmed to bend girders for suicide booths, and is later designated as assistant sales manager and cook, despite lacking a sense of taste. He is Fry's best friend and roommate.
- Professor Hubert J. Farnsworth (Billy West)
- Professor Hubert Farnsworth, also known simply as "the Professor," is Fry's distant nephew.[56] Farnsworth founded Planet Express Inc. to fund his work as a mad scientist. Although he is depicted as a brilliant scientist and inventor, at more than one-hundred and sixty years old he is extremely prone to age-related forgetfulness and fits of temper. In the episode "A Clone of My Own," the Professor clones himself to produce a successor, Cubert Farnsworth, whom he treats like a son.
- Dr. John A. Zoidberg (Billy West)
- Zoidberg is a lobster-like alien from the planet Decapod 10, and the neurotic staff physician of Planet Express. Although he claims to be an expert on humans, his knowledge of human anatomy and physiology is woefully inaccurate. Zoidberg is homeless, penniless, and—despite being depicted as Professor Farnsworth's long-time friend—held in contempt by everyone on the crew, except Fry.
- Amy Wong (Lauren Tom)
- Amy is an incredibly rich, blunt, spoiled, ditzy, and accident-prone long-term intern at Planet Express. She is an engineering student at Mars University and heiress to the western hemisphere of Mars. Born on Mars, she is ethnically Chinese and is prone to cursing in Cantonese and using 31st-century slang. Her parents are the wealthy ranchers Leo and Inez Wong. She is promiscuous in the beginning of the series and eventually enters a monogamous relationship with Kif Kroker. In the show's sixth season, she acquires her doctorate.
- Hermes Conrad (Phil LaMarr)
- Hermes is the Jamaican accountant of Planet Express. A 36th-level bureaucrat (promoted to level 34 during the series) and proud of it, he is a stickler for regulation and enamored of the tedium of paperwork and bureaucracy. Hermes is also a former champion in Olympic Limbo, a sport derived from the popular party activity. He gave up limbo after the 2980 Olympics when a young fan, imitating him, broke his back and died. Hermes has a wife, LaBarbara, and a 12-year-old son, Dwight.
- Zapp Brannigan (Billy West)
- Zapp Brannigan is the incompetent, extraordinarily vain captain of the DOOP starship Nimbus. He is a satirical pastiche of Captain Kirk and William Shatner. Although Leela thoroughly detests him, Brannigan—a self-deluded lady's man—pursues her relentlessly, often at great personal risk. Brannigan was dishonorably dismissed from the DOOP in Brannigan Begin Again but was reinstated in the same episode. He was originally going to be voiced by Phil Hartman, but Hartman died before production could begin.
- Kif Kroker (Maurice LaMarche)
- Zapp Brannigan's 4th Lieutenant and long-suffering personal assistant, Kif is a member of the amphibious species that inhabits the planet Amphibios 9. Although extremely timid, he eventually works up the courage to date Amy. Kif is often shown sighing in disgust at the nonsensical rantings of his commanding officer.
- Mom (Tress MacNeille)
- Mom is the malevolent, foul-mouthed, cruel, and narcissistic owner of MomCorp, the thirtieth century's largest shipping and manufacturing company, with a monopoly on robots. In public, she maintains the image of a sweet, kindly old woman by speaking in stereotypically antiquated statements and wearing a mechanical fat suit. She occasionally launches insidious plans for world domination and corporate takeover. She has a romantic history with the Professor which left her bitter and resentful. She has three bumbling sons, Walt, Larry, and Igner (modeled after the Three Stooges), who do her bidding despite frequent abuse, and often infuriate her with their incompetence. In Bender's Game, it is revealed that Igner's father is Professor Farnsworth.
- Nibbler (Frank Welker)
- Nibbler is Leela's pet Nibblonian, whom she rescued from an imploding planet and adopted early in the series. Despite his deceptively cute exterior, Nibbler is actually a highly intelligent super-being whose race is responsible for maintaining order in the universe. He is revealed in "The Why of Fry" to have been directly responsible for Fry's cryogenic freezing. While the size of an average house cat, his race is capable of devouring much larger animals and excretes dark matter, which until Bender's Game is used as fuel for space cruisers in the series.
Setting
Futurama is set in New New York at the turn of the 31st century, in a time filled with technological wonders. The city of New New York has been built over the ruins of present-day New York City, referred to as "Old New York." Various devices and architecture are similar to the Populuxe style. Global warming, inflexible bureaucracy, and substance abuse are a few of the subjects given a 31st-century exaggeration in a world where the problems have become both more extreme and more common. Just as New York has become a more extreme version of itself in the future, other Earth locations are given the same treatment, like Los Angeles being depicted as a smog filled apocalyptic wasteland.
Numerous technological advances have been made between the present day and the 31st century. The ability to keep heads alive in jars was invented by Ron Popeil (who has a guest cameo in "A Big Piece of Garbage"), which has resulted in many historical figures and current celebrities being present, including Groening himself; this became the writers' device to feature and poke fun at contemporary celebrities in the show. Curiously, several of the preserved heads shown are those of people who were already dead well before the advent of this technology; one of the most prominent examples of this anomaly is frequent Earth president Richard Nixon, who died in 1994. The Internet, while being fully immersive and encompassing all senses — even featuring its own digital world (similar to Tron or The Matrix) — is slow and largely consists of pornography, pop-up ads, and "filthy" (or Filthy Filthy) chat rooms. Some of it is edited to include educational material ostensibly for youth. Television is still a primary form of entertainment. Self-aware robots are a common sight, and are the main cause of global warming thanks to their alcohol-powered systems. The wheel is obsolete (no one but Fry even seems to recognize the design),[57] having been forgotten and replaced by hover cars and a network of large, clear pneumatic transportation tubes.
Environmentally, common animals still remain, alongside mutated, cross-bred (sometimes with humans) and extraterrestrial animals. Ironically, Spotted Owls are often shown to have replaced rats as common household pests. Although rats still exist, sometimes rats act like pigeons. Pigeons still exist, as well. Pine trees, anchovies and poodles have been extinct for 800 years. Earth still suffers the effects of greenhouse gases, although in one episode Leela states that its effects have been counteracted by nuclear winter. In another episode, the effects of global warming have been somewhat mitigated by the dropping of a giant ice cube into the ocean, and later by pushing Earth farther away from the sun.
Futurama's setting is a backdrop, and the writers are not above committing continuity errors if they serve to further the gags. For example, while the pilot episode implies that the previous Planet Express crew was killed by a space wasp, the later episode "The Sting" is based on the crew having been killed by space bees instead.[58] The "world of tomorrow" setting is used to highlight and lampoon issues of today and to parody the science fiction genre.[59]
Themes
Earth is depicted as being multicultural to the extent that a wide range of human, robot, and extraterrestrial beings interact with the primary characters. In some ways the future is depicted as being more socially advanced than Fry's, and therefore the audience's, reality. However, it is often shown to have many of the same types of problems, challenges, mistakes, and prejudices as the present.
Robots make up the largest "minority". Most robots are self-aware and have been granted freedom and self-determination, but while a few are depicted as wealthy members of the upper class, they are often treated as second-class citizens.[57] Likewise, robot–human relationships (termed "robosexual") are stigmatized,[60] and robot–human marriages are initially depicted as illegal.[61] Sewer mutants are mutated humans who must live in the sewers by law. They are initially depicted as holding urban legend status and regarded as fictional by most members of the public. This was contradicted by later episodes that depict Earth society as having enforced laws regarding mutants. However, since the conclusion of Season Six, mutants have been granted full status as citizens and are therefore granted the same rights to surface use as normal humans.
Religion is still a prominent part of society, although the dominant religions have evolved. A merging of the major religious groups of the 20th century has resulted in the First Amalgamated Church,[62] while Voodoo is now mainstream. New religions include Oprahism, Robotology, and the banned religion of Star Trek fandom. Religious figures include Father Changstein-El-Gamal, the Robot Devil, Reverend Preacherbot, and passing references to the Space Pope, who appears to be a large crocodile-like creature. While very few episodes focus exclusively on religion within the Futurama universe, they do cover a wide variety of subjects including predestination, prayer, the nature of salvation, and religious conversion.[62]
Earth has a unified government headed by the President of Earth. Richard Nixon's head is elected to the position in Season Two, and holds the office in subsequent episodes. Earth's capital is Washington, D.C., and the flag of Earth is similar in design to the flag of the United States, with the western hemisphere displayed in place of the fifty stars. The show is set mostly in the former United States, and other parts of the world are rarely shown. Citizens of Earth are referred to as "Earthicans," and English is shown to be the primary language of almost every sentient species.
The Democratic Order of Planets (D.O.O.P.) has been compared to both the United Nations and the United Federation of Planets of the Star Trek universe.[63] Numerous other galaxies have been colonized or have made contact by the year 3000. Mars has been terraformed and is home to Mars University, Mars Vegas, and tribes similar to Native Americans, though they departed upon learning that the "worthless bead" they traded their land for (the Martian surface) was actually a giant diamond worth a fortune, deciding to buy another planet and act like it is sacred.
A derivative of baseball, called blernsball, is played, and the New New York Mets, a laughingstock of the league, still play in Shea Stadium. A New New York Yankees team also exists.
Due to the fact that the world of Fry's time was destroyed, much of the knowledge of history before then was lost. In the 31st century, facts gathered by archaeologists are portrayed as grossly inaccurate. For example, in "The Lesser of Two Evils", the theme park "Past-O-Rama" presents a history in which 20th-century car factories had assembly lines in which cars were not assembled by giant robotic welding arms, but by robots dressed like stereotypical cavemen. Another example comes from "The Series Has Landed", in which knowledge of the Moon Landing has been lost for centuries. As a result, archaeologists came to the conclusion that the idea to go to the moon came from the infamous quote from The Honeymooners.
Hallmarks
Opening sequence
Much like the opening sequence in The Simpsons with its chalkboard, sax solo, and couch gags, Futurama has a distinctive opening sequence featuring minor gags. As the show begins, blue lights fill the screen and the Planet Express ship flies across the screen with the title of the show being spelled out in its wake. Underneath the title is a joke caption such as "Painstakingly drawn in front of a live studio audience." or "When you see the robot: DRINK!"[64] After flying through downtown New New York and past various recurring characters, the Planet Express ship crashes into a large screen showing a short clip from a classic cartoon. These have included clips from Looney Tunes shorts, cartoons produced by Max Fleischer, a short of The Simpsons from a Tracey Ullman episode,[65] and the show's own opening sequence in "The Devil's Hands Are Idle Playthings". Most episodes in Season 6 use a significantly shortened opening sequence, omitting the brief clip of a classic cartoon. Several episodes begin with a cold opening before the opening sequence, although these scenes do not always correspond with the episode's plot. The opening sequence has been lampooned several times within the show, in episodes including "That's Lobstertainment!", "The Problem with Popplers", as "Future-roma" in "The Duh-Vinci Code" and as "Futurella" in "Lrrreconcilable Ndndifferences".
Series director Scott Vanzo has remarked on the difficulty of animating the sequence. It took four to five weeks to fully animate the sequence, and it consists of over 80 levels of 3D animation composited together.[66] It takes approximately one hour to render a single frame, and each second of the sequence consists of around 30 frames.[67]
Bender's Big Score has an extended opening sequence, introducing each of the main characters. In The Beast with a Billion Backs and Bender's Game the ship passes through the screen's glass and temporarily becomes part of the environment depicted therein—a pastiche of Disney's Steamboat Willie and Yellow Submarine respectively—before crashing through the screen glass on the way out. In Into the Wild Green Yonder, a completely different opening sequence involves a trip through a futuristic version of Las Vegas located on Mars. The theme tune is sung by Seth MacFarlane and is different from the standard theme tune. The end of the film incorporates a unique variation of the opening sequence; as the Planet Express ship enters a wormhole, it converts into a pattern of lights similar to the lights that appear in the opening sequence.
The Futurama theme was created by Christopher Tyng. The theme is played on the tubular bells but is occasionally remixed for use in specific episodes, including a version by the Beastie Boys used for the episode "Hell Is Other Robots", in which they guest starred.[64] The theme also samples a drum break originating from "Amen, Brother" by American soul group The Winstons; however, the drum break is replaced in Season 6. A remixed rendition of the theme is used in Season 5, which features altered instruments and a lower pitch. Season 6 also uses this remix, but it has been reduced again in pitch and tempo.
Language
There are three alternative alphabets that appear often in the background of episodes, usually in the forms of graffiti, advertisements, or warning labels. Nearly all messages using alternative scripts transliterate directly into English. The first alphabet consists of abstract characters and is referred to as Alienese,[54] a simple substitution cipher from the Latin alphabet.[68] The second alphabet uses a more complex modular addition code, where the "next letter is given by the summation of all previous letters plus the current letter."[69] The codes often provide additional jokes for fans dedicated enough to decode the messages.[59] The third language sometimes used is Hebrew. Aside from these alphabets, most of the displayed wording on the show uses the Latin alphabet.
Several English expressions have evolved since the present day. For example, the word Christmas has been replaced with Xmas (pronounced "ex-mas"), and the word ask with aks (pronounced axe). According to David X. Cohen it is a running joke that the French language is extinct in the Futurama universe (though the culture remains alive), much like Latin is in the present.[70] In the French dubbing of the show, German is used as the extinct language instead.
Humor
Although the series uses a wide range of styles of humor, including self-deprecation, black comedy, off-color humor, slapstick, and surreal humor, its primary source of comedy is its satirical depiction of everyday life in the future and its parodical comparisons to the present.[52] Matt Groening notes that, from the show's conception, his goal was to make what was, on the surface, a goofy comedy that would have underlying "legitimate literary science fiction concepts."[71] The series contrasted "low culture" and "high culture" comedy; for example, Bender's catchphrase is the insult "Bite my shiny metal ass" while his most terrifying nightmare is a vision of the number 2, a joke referencing the binary numeral system (Fry assures him, "there's no such thing as two.").[52]
The series developed a cult following partially due to the large number of in-jokes it contains, most of which are aimed at "nerds."[52] In commentary on the DVD releases, David X. Cohen points out and sometimes explains his "nerdiest joke[s]."[72] These included mathematical jokes — such as "Loew's 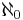 -plex" (aleph-null-plex) movie theater,[72] — as well as various forms of science humor — for example, Professor Farnsworth, at a racetrack, complains about the use of a quantum finish to decide the winner "No fair! You changed the outcome by measuring it," a reference to the observer effect in quantum mechanics.[73] In the season six episode "Law and Oracle", Fry and the robot peace officer URL track down a traffic violator who turns out to be Erwin Schrödinger, the 20th century quantum physicist. On the front seat of the car is a box, and when questioned about the contents, Schrödinger replies "A cat, some poison, and a Caesium atom." Fry asks if the cat is alive or dead, and Schrodinger answers "It's a superposition of both states until you open the box and collapse the wave function." The run is a reference to the Schrödinger's cat thought experiment of quantum mechanics. The series makes passing references to quantum chromodynamics (the appearance of Strong Force-brand glue),[74] computer science (two separate books in a closet labeled P and NP respectively, referring to the possibility that P and NP-complete problem classes are distinct),[75] electronics (an X-ray — or more accurately, an "F-ray" — of Bender's head reveals a 6502 microprocessor),[76] and genetics (a mention of Bender's "robo- or R-NA").[77] The show often features subtle references to classic science fiction. These are most often to Star Trek — many soundbites are used in homage[52] — but also include the reference to the origin of the word robot made in the name of the robot-dominated planet Chapek 9,[78] and the black rectangular monolith labeled "Out of Order" in orbit around Jupiter (a reference to Arthur C. Clarke's Space Odyssey series).[79] Bender and Fry sometimes watch a television show called The Scary Door, a humorous pastiche of The Twilight Zone.[80]
-plex" (aleph-null-plex) movie theater,[72] — as well as various forms of science humor — for example, Professor Farnsworth, at a racetrack, complains about the use of a quantum finish to decide the winner "No fair! You changed the outcome by measuring it," a reference to the observer effect in quantum mechanics.[73] In the season six episode "Law and Oracle", Fry and the robot peace officer URL track down a traffic violator who turns out to be Erwin Schrödinger, the 20th century quantum physicist. On the front seat of the car is a box, and when questioned about the contents, Schrödinger replies "A cat, some poison, and a Caesium atom." Fry asks if the cat is alive or dead, and Schrodinger answers "It's a superposition of both states until you open the box and collapse the wave function." The run is a reference to the Schrödinger's cat thought experiment of quantum mechanics. The series makes passing references to quantum chromodynamics (the appearance of Strong Force-brand glue),[74] computer science (two separate books in a closet labeled P and NP respectively, referring to the possibility that P and NP-complete problem classes are distinct),[75] electronics (an X-ray — or more accurately, an "F-ray" — of Bender's head reveals a 6502 microprocessor),[76] and genetics (a mention of Bender's "robo- or R-NA").[77] The show often features subtle references to classic science fiction. These are most often to Star Trek — many soundbites are used in homage[52] — but also include the reference to the origin of the word robot made in the name of the robot-dominated planet Chapek 9,[78] and the black rectangular monolith labeled "Out of Order" in orbit around Jupiter (a reference to Arthur C. Clarke's Space Odyssey series).[79] Bender and Fry sometimes watch a television show called The Scary Door, a humorous pastiche of The Twilight Zone.[80]
Journalist/critic Frank Lovece in Newsday contrasted the humor tradition of Groening's two series, finding that, "The Simpsons echoes the strains of American-Irish vaudeville humor — the beer-soaked, sneaking-in-late-while-the-wife's-asleep comedy of Harrigan and Hart, McNulty and Murray, the Four Cohans (which, yes, included George M.) and countless others: knockabout yet sentimental, and ultimately about the bonds of blood family. Futurama, conversely, stems from Jewish-American humor, and not just in the obvious archetype of Dr. Zoidberg. From vaudeville to the Catskills to Woody Allen, it's that distinctly rueful humor built to ward away everything from despair to petty annoyance — the 'You gotta do what you gotta do' philosophy that helps the 'Futurama' characters cope in a mega-corporate world where the little guy is essentially powerless".[48] Animation maven Jerry Beck concurred: "I'm Jewish, and I know what you're saying. Fry has that [type of humor], Dr. Zoidberg, all the [vocal artist] Billy West characters. I see it. The bottom line is, the producers are trying to make sure the shows are completely different entities".[48]
Reception, legacy, and achievements
Success
Futurama's 7:00 p.m. Sunday timeslot caused the show to often be pre-empted by sports and usually have a later than average season premiere. It also allowed the writers and animators to get ahead of the broadcast schedule so that episodes intended for one season were not aired until the following season. By the beginning of the fourth broadcast season, all the episodes to be aired that season had already been completed and writers were working at least a year in advance.[18]
When Futurama debuted in the Fox Sunday night line-up at 8:30 p.m. between The Simpsons and The X-Files on March 28, 1999, it managed 19 million viewers. Tying for 11th overall in that week's Nielsen ratings.[81] The following week, airing at the same time, Futurama drew 14.2 million viewers. The third episode, the first airing on Tuesday, drew 8.85 million viewers.[82] Though its ratings were well below The Simpsons, the first season of Futurama rated higher than competing animated series: King of the Hill, Family Guy, Dilbert, South Park, and The PJs.[83]
When Futurama was effectively canceled in 2003, it had averaged 6.4 million viewers for the first half of its fourth broadcast season.[84]
In late 2002, Cartoon Network acquired exclusive cable syndication rights to Futurama for a reported ten million dollars.[85] In January 2003,[85] the network began airing Futurama episodes as the centerpiece to the expansion of their Adult Swim cartoon block. In October 2005, Comedy Central picked up the cable syndication rights to air Futurama's 72-episode run at the start of 2008, following the expiration of Cartoon Network's contract.[35] It was cited as the largest and most expensive acquisition in the network's history. It is currently airing every night, followed by South Park.[86] A Comedy Central teaser trailer announced the return of Futurama March 23, 2008,[87] which was Bender's Big Score divided into four episodes followed by the other three movies. The series also airs in syndication in many countries around the world.
On June 24, 2010, the season six premiere, "Rebirth", drew 2.92 million viewers in the 10 p.m. timeslot, on Comedy Central.[88] The second episode of the sixth season, "In-A-Gadda-Da-Leela", aired at 10:30 p.m., immediately following the season premiere. "In-A-Gadda-Da-Leela" drew 2.78 million viewers.[88] This was the series' premiere on the network, with original episodes—the fifth season had previously aired on the network, but it had originally been released in the form of the four direct-to-video films.
Awards
| Wins[89] | Nominations[89] | |
|---|---|---|
Annie Awards:
Writers Guild of America Award:
|
Annie Awards:
|
Emmy Awards:
Writers Guild of America Award:
|
Achievements
- The Futurama Theorem
On August 19, 2010, Comedy Central aired "The Prisoner of Benda", an episode written by Ken Keeler. To support the plot of this episode, Keeler, a PhD mathematician, penned "The Futurama Theorem", a mathematical proof which proves the properties of an irreversible body swap scenario.
- Other honors
In January 2009, IGN named Futurama as the 8th best in the "Top 100 Animated TV Series".[94]
At the 2010 San Diego Comic-Con International, Guinness World Records presented Futurama with the record for "Current Most Critically Acclaimed Animated Series".[7]
Other media
Comic books
First started in November 2000, Futurama Comics is a comic book series published by Bongo Comics based in the Futurama universe.[95] While originally published only in the US, a UK, German and Australian version of the series is also available.[96] In addition, three issues were published in Norway. Other than a different running order and presentation, the stories are the same in all versions. While the comics focus on the same characters in the Futurama fictional universe, the comics may not be canonical as the events portrayed within them do not necessarily have any effect upon the continuity of the show.
Like the TV series, each comic (except US comic #20) has a caption at the top of the cover. For example: "Made In The USA! (Printed in Canada)." Some of the UK and Australian comics have different captions on the top of their comics (for example, the Australian version of #20 says "A 21st Century Comic Book" across the cover, while the US version does not have a caption on that issue). All series contain a letters page, artwork from readers, and previews of other upcoming Bongo comics.
Films
When Comedy Central began negotiating for the rights to air Futurama reruns, Fox suggested that there was a possibility of also creating new episodes. Negotiations were already underway with the possibility of creating two or three straight-to-DVD films. When Comedy Central committed to sixteen new episodes, it was decided that four films would be produced.[36] On April 26, 2006, Groening noted in an interview that co-creator David X. Cohen and numerous writers from the original series would be returning to work on the movies.[97] All the original voice actors participated. In February 2007, Groening explained the format of the new stories: "[The crew is] writing them as movies and then we're going to chop them up, reconfigure them, write new material and try to make them work as separate episodes."[98]
The first movie, Futurama: Bender's Big Score, was written by Ken Keeler and Cohen, and includes return appearances by the Nibblonians, Seymour, Barbados Slim, Robot Santa, the "God" space entity, Al Gore, and Zapp Brannigan.[99] It was animated in widescreen and was released on standard DVD on November 27, 2007, with a possible Blu-ray Disc release to follow.[100] A release on HD DVD was rumored but later officially denied. Futurama: Bender's Big Score was the first DVD release for which 20th Century Fox implemented measures intended to reduce the total carbon footprint of the production, manufacturing, and distribution processes. Where it was not possible to completely eliminate carbon, output carbon offsets were used, thus making the complete process carbon neutral.[101]
The second movie, The Beast with a Billion Backs, was released on June 24, 2008. The third movie, Bender's Game, was released on DVD and Blu-ray Disc[102] on November 3, 2008 in the UK, November 4, 2008 in the USA, and December 10, 2008 in Australia. The fourth movie, Into the Wild Green Yonder, was released on DVD and Blu-ray Disc on February 23, 2009.[103]
Video game
On September 15, 2000, Unique Development Studios acquired the license to develop a Futurama video game for consoles and handheld systems. Fox Interactive signed on to publish the game.[104] Sierra Entertainment later became the game's publisher, and it was released on August 14, 2003.[105] Versions are available for PlayStation 2 and Xbox, both of which use cel-shading technology; however, the game was subsequently canceled on the Nintendo GameCube and Game Boy Advance in North America and Europe.[106]
International broadcast
| Country / Region | Network(s) | Aired | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Fox Comedy Central Adult Swim |
March 28, 1999 – August 10, 2003 March 23, 2008 – present January 1, 2003 – December 31, 2007 |
Fox does not currently air the series. Comedy Central currently airs new episodes of the series.[107] Adult Swim does not currently air the series. |
| United Kingdom | Sky1 | – present | Sky1 currently airs new episodes of the series.[108] |
| Italy | Fox | – present | Fox currently airs the series in Italy. |
| Canada | Teletoon at Night Global Television |
– present March 28, 1999 – August 10, 2003 |
Teletoon at Night currently airs the series.[109] Global does not currently air the series. |
Merchandise
While relatively uncommon, several action and tin figurines of various characters and items from the show have been made and are being sold by various hobby/online stores. When the show was initially licensed, plans were made with Rocket USA to produce wind-up, walking tin figurines of both Bender and Nibbler with packaging artwork done by the original artists for the series.[110] The Bender toy included a cigar and bottle of "Olde Fortran Malt Liquor" and featured moving eyes, antenna, and a functioning compartment door; it received an "A" rating from Sci Fi Weekly.[111] A can of Slurm cola actually contains a deck of cards featuring the Planet Express crew as the face cards. A two-deck pack of cards was also released.
I-Men released five two-packs of 2.5-inch (64 mm) high figures: Fry and Calculon; Zoidberg and Morbo; Professor Farnsworth and URL; Robot Devil and Bender; Leela and Roberto. Each figure comes with a corresponding collectable coin that can also double as a figure stand.
The collectible releases include a set of bendable action figures, including Lieutenant Kif Kroker, Turanga Leela, and Bender. There have also been a few figures released by Moore Action Collectibles, including Fry, Turanga Leela, Bender, and the Planet Express ship. In late 2006, Rocket USA brought out a limited edition "super" heavyweight die-cast Bender. Another special edition Bender figure was released at the San Diego Comic Con (SDCC) in 2006; the figure was called "Glorious Golden Bender."
Toynami is currently producing new Futurama figures.[112] The first series of the Toynami figures is separated into 3 waves: wave one, released in September 2007, featured Fry and Zoidberg; wave two, released in January 2008, consisted of Leela and Zapp (who comes with Richard Nixon's head-in-a-jar); the third wave, released in June 2008, includes Bender and Kif. Each figure comes with a build-a-figure piece to assemble the Robot Devil. The second series of Toynami figures includes Captain Yesterday (A Fry variant from "Less Than Hero") and Nudar in the first wave. The second wave includes Super-King (Bender from "Less Than Hero") and Calculon, and the third wave includes Clobberella (Leela from "Less Than Hero") and Amy Wong. The figures in series 2 include pieces to build Robot Santa. The third, and current, series of the Toynami line includes Professor Farnsworth (who comes with Nibbler), and Hermes. Wave 2 was released in February 2010 and includes Chef Bender and Mom, who comes with a removable fat-suit. Series 3 figures come with pieces to build Roberto. Series 9 will include URL and Wooden Bender (from "Obsoletely Fabulous") and Series 10 will include Clamps and Joey Mousepad. Series 11 consists of The Donbot and Flexo. That wave will not have a specific Build A Bot character, planned Morbo. All figures feature multiple points of articulation and character-specific accessories.
In August 2009 Kidrobot released 3-inch vinyl mini figurines of some of the cast. These are sold in "blind" box form and each comes with an accessory. Probability of receiving each of the characters is printed on the side, with two special mystery characters having unknown probabilities.
See also
| Book: Futurama | |
| Wikipedia books are collections of articles that can be downloaded or ordered in print. | |
Notes
- ^ "Groening's Bargain to Yield Four Futurama Movies". Reuters. 2007-01-28. http://www.rottentomatoes.com/news/1648183/. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ Wallenstein, Andrew (2006-06-22). ""Futurama" gets new life on Comedy Central". Reuters. Archived from the original on 2006-06-11. http://web.archive.org/web/20061106224128/http://entertainment.tv.yahoo.com/entnews/va/20060622/115104459800.html. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ "Comedy Central's 'South Park,' 'Lil' Bush,' More to Return in March". 08-02-07. http://www.thefutoncritic.com/news.aspx?id=7549. Retrieved 2008-11-08.
- ^ Josef Adalian and Vlada Gelman (2010-02-02). "Things Are Looking Good for Another Season of Futurama". Vulture. http://nymag.com/daily/entertainment/2011/02/futurama_renewed.html. Retrieved 2010-02-28.
- ^ a b James Hibberd (2011-03-24). "'Futurama' renewed for two more years!". http://insidetv.ew.com/2011/03/24/futurama-renewed/. Retrieved 2011-03-24.
- ^ "COMEDY CENTRAL® RENEWS "FUTURAMA" FOR 26 NEW EPISODES". March 29, 2011. http://www.comedycentral.com/press/press_releases/2011/032811_futurama-renewed-for-26-new-episodes.jhtml. Retrieved March 30, 2011.
- ^ a b Cordova, Gonzalo (July 24, 2010). "Comedy Central At Comic-Con: Day Three, Futurama Panel". Comedy Central Insider. Comedy Central. http://ccinsider.comedycentral.com/2010/07/24/comedy-central-at-comic-con-day-three-futurama-panel/. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- ^ Abalos, Nelson (July 25, 2010). "Comic Con 2010 Futurama Sets Guinness World Record". PixelatedGeek.com. http://pixelatedgeek.com/2010/07/comic-con-futurama-sets-guinness-world-record/. Retrieved 4 September 2010.
- ^ Needham, Alex (October 1999). "Nice Planet...We'll Take It!". The Face (33). http://web.archive.org/web/20000824051707/www.frcr.com/library/the_face1.html.
- ^ Doherty, Brian (March /April 1999). "Matt Groening". Mother Jones. http://www.motherjones.com/media/1999/03/matt-groening. Retrieved January 14, 2007.
- ^ a b c Needham, Alex (October 1999). "Nice Planet...We'll Take It!". http://web.archive.org/web/20000824051707/www.frcr.com/library/the_face1.html. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ Snierson, Dan (1999-03-26). "Space Case". Entertainment Weekly. http://web.archive.org/web/20000824042829/www.frcr.com/library/ew_online1.html. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ "Groening Bites the Hand that Feeds". Mr. Showbiz. 1999-04-08. http://web.archive.org/web/20000824051817/www.frcr.com/library/mrshowbiz1.html. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ Taylor, Timothy Dean (2001). Strange Sounds: Music, Technology & Culture. pp. 104–105. ISBN 0415936845.
- ^ Cohen, David X.; Groening, Moore, Rich; Vanzo, Gregg; DiMaggio, John (2002). Futurama: Volume One DVD commentary for the episode "Fear of a Bot Planet" (DVD). 20th Century Fox. "Groening: The original name for this show was not "Futurama", by the way. There was a long long list of possible names, the only two I remember which were resoundly rejected, by everyone concerned with it; "Doomsville" was my number one choice. And my number two choice — and I don't even know why I thought this was a good idea for a name — somehow, "Aloha, Mars" struck me and that was also not particularly..."
- ^ Fitzpatrick, Kevin (August 4, 2011). "Futurama Facts You Never Knew". UGO. http://www.ugo.com/tv/futurama-facts-you-never-knew. Retrieved 5 August 2011.
- ^ Saunders, Dusty (1999-03-25). "Fox's far-out Futurama looks like a hit". Denver Rocky Mountain News. http://web.archive.org/web/20000824051917/www.frcr.com/library/denver1.html. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ a b c "David X. Cohen boards the Planet Express to find meaning in Futurama". Sci Fi Weekly. December 17, 2001. Archived from the original on June 10, 2008. http://web.archive.org/web/20080610080245/http://www.scifi.com/sfw/interviews/sfw7897.html. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ "Online Chat with Matt Groening". TV Guide. 1999-04-06. http://web.archive.org/web/20000929144303/frcr.com/library/april6_matt_g_chat.html. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ "David X Cohen interview with GotFuturama.com". http://www.gotfuturama.com/Information/Articles/DavidInterview/DavidXCohenInterview.dhtml. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ a b c d e f Ken P. (2005-08-22). "IGN Interviews Billy West". http://uk.tv.ign.com/articles/652/652770p1.html. Retrieved 2005-08-22.
- ^ a b c Joel Keller (2006-06-15). "Billy West: The TV Squad Interview". http://www.tvsquad.com/2006/06/15/billy-west-the-tv-squad-interview. Retrieved 2007-10-25.
- ^ a b Itzkoff, Dave (2010-06-24). "‘Futurama’-Rama: Welcome Back to the World of Tomorrow". The New York Times. http://artsbeat.blogs.nytimes.com/2010/06/24/futurama-rama-welcome-back-to-the-world-of-tomorrow/. Retrieved 2010-07-08.
- ^ Cohen, David X (2003). Futurama season 1 DVD commentary for the episode "Space Pilot 3000" (DVD). 20th Century Fox.
- ^ Dimaggio, John (2003). Futurama season 1 DVD commentary for the episode "Space Pilot 3000" (DVD). 20th Century Fox.
- ^ "Scott Vanzo of Rough Draft Studios e-mail response". http://www.peelified.com/Futurama-Forum-1/Topic-520-0-D_Animation_in_Futurama.html. Retrieved 2001-06-20.
- ^ "'Futurama' Producer David X. Cohen Talks Holiday Special". 2010-11-19. http://tv.yahoo.com/news/article/ustv.associatedcontent.com/ustv.associatedcontent.com-futurama-producer-david-x-cohen-talks-holiday-special. Retrieved 2010-11-29.
- ^ Duncan, Andrew (1999-09-24). "Matt Groening Interview with Radio Times". Radio Times. http://web.archive.org/web/20000824042839/www.frcr.com/library/radio_times1.html. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ Villanueva, Annabelle (September–October 1999). "Fall TV Preview: Tricks and Treats". Cinescape. http://web.archive.org/web/20000929143556/frcr.com/library/cinescape1.html. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ Winer, Adam (1999-12-09). "Futurama Shock". Entertainment Weekly. http://web.archive.org/web/20000824051659/www.frcr.com/library/ew_online3.html. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ "UPDATE UPDATED!! FUTURAMA Thing of the Past?? Or What??". Ain't It Cool News. February 12, 2002. http://www.aintitcool.com/display.cgi?id=11499. Retrieved 2006-06-14.
- ^ "'Out of their minds': Groening savages TV execs". Chortle. 2003-03-19. http://www.chortle.co.uk/news/2003/03/19/2684/out_of_their_minds. Retrieved 2009-04-09.
- ^ "Fox Says 'No' to 'Futurama'". Zap2it. February 12, 2002. Archived from the original on 2003-10-14. http://web.archive.org/web/20031014031053/http://tv.zap2it.com/tveditorial/tve_main/1,1002,271. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ "Remeber(sic) Me after my Death!". Can't Get Enough Futurama. May 15, 2003. http://www.gotfuturama.com/Futurama/News/1053009995,66450,/. Retrieved 2008-06-03. [sic]
- ^ a b "Adult Swim". Cartoon Network Pressroom. Archived from the original on 2008-01-02. http://web.archive.org/web/20080102142245/http://www.turnerinfo.com/programinfoitem.aspx?P=CARTOON&CID01=f1f70fce-1735-493e-bdeb-7f2755eb5c8c&CID02=f1f70fce-1735-493e-bdeb-7f2755eb5c8c. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ a b Katz, Claudia (2007-11-16). Exclusive Interview: Claudia Katz on Futurama the Movie: Bender's Big Score. Interview with Evan Jacobs. http://www.movieweb.com/news/NEyTuBCyy6XECD. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ Wortham, Jenna (2008-11-04). "Futurama Animators Roll 20-Sided Die With Bender's Game". Wired.com. http://blog.wired.com/underwire/2008/11/futuramas-anima.html. Retrieved 2009-02-28.
- ^ Leopold, Todd (2009-02-26). "Matt Groening looks to the future". CNN.com. http://www.cnn.com/2009/SHOWBIZ/TV/02/26/matt.groening.futurama/index.html. Retrieved 2009-03-17.
- ^ Ausiello, Michael (2009-06-09). "It's official: 'Futurama' is reborn!". Entertainment Weekly. http://ausiellofiles.ew.com/2009/06/its-official-futurama-returns.html. Retrieved 2009-06-09.
- ^ "'Futurama' Returns to Production with an initial order of 26 New Episodes to Premiere Mid 2010". Press Central Comedy Central Press Release. 2009-06-10. http://www.comedycentral.com/press/press_releases/2009/061009_futurama_returns.jhtml. Retrieved 2009-06-24.
- ^ Goldman, Eric (2009-06-09). "Futurama Return Made Official". IGN. http://uk.tv.ign.com/articles/993/993144p1.html. Retrieved 2009-06-10.
- ^ Schneider, Michael (2009-06-09). "'Futurama' returns with new episodes". Variety. http://www.variety.com/article/VR1118004722.html?categoryid=14&cs=1. Retrieved 2009-06-14.
- ^ Schneider, Michael (2009-07-17). "'Futurama' without original voices?". Variety. http://www.variety.com/article/VR1118006123.html?categoryid=14&cs=1. Retrieved 2009-07-18.
- ^ Keith Phipps (2009-07-29). "Comic con day 3:cartoon capers ect.". A.V.Club.com. http://www.avclub.com/articles/comic-con-day-3-cartoon-capers-and-the-ongoing-fut,30860/. Retrieved 2009-07-29.
- ^ "Save the Voices of Futurama". 2009-07-31. http://www.facebook.com/home.php#/group.php?gid=216285555057. Retrieved 2009-07-31.
- ^ Salem, Rob. "Futurama cast members ink new deal with Fox", TheStar.com, July 31, 2009
- ^ Frucci, Adam (2009-08-25). "Futurama Returning with Full Original Cast After All". Gizmodo. http://gizmodo.com/5345037/futurama-returning-with-full-original-cast-after-all. Retrieved 2009-08-25.
- ^ a b c d Lovece, Frank. "'Futurama' finds a new future on Comedy Central", Newsday, August 28, 2009; posted online August 27, 2009
- ^ Gough, Paul J. (June 29, 2010). ""Futurama" returns with strong ratings". Yahoo! News. http://news.yahoo.com/s/nm/20100629/tv_nm/us_futurama. Retrieved 1 July 2010.
- ^ "WGN America Fall 2011 Schedule; MeTV Network Celebrates Lucille Ball's 100th Birthday With 100 Episodes of Lucy Series". Blog.sitcomsonline.com. 2011-07-26. http://blog.sitcomsonline.com/2011/07/wgn-america-fall-2011-schedule-metv.html. Retrieved 2011-08-23.
- ^ "Futurama". wgnamerica. 2011-10-19. http://www.wgnamerica.com/shows/futurama. Retrieved 2011-11-01.
- ^ a b c d e f Cook, Lucius (2004-04-26). "Hey, Sexy Mama, Wanna Kill All Humans?: Looking Backwards at Futurama, The Greatest SF Show You've Never Seen". Locus Online. http://www.locusmag.com/2004/Reviews/04Cook_Futurama.html. Retrieved 2008-07-29.
- ^ Gates, Anita (1999-01-24). "Groening's New World, 1,000 Years From Springfield". The New York Times. http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9800EFD61530F937A15752C0A96F958260&sec=&spon=&pagewanted=2. Retrieved 2008-06-13.
- ^ a b "Leela's Homeworld". Futurama. Fox Network. 2002-02-17. No. 12, season 4.
- ^ "Futurama" (1999) - Trivia
- ^ "A Clone of My Own". Futurama. Fox Network. 2000-04-09. No. 10, season 2. 3 minutes in.
- ^ a b "Mother's Day". Futurama. Fox Network. 2000-05-14. No. 14, season 2.
- ^ Verrone, Patric M (2003), DVD commentary for "The Sting", Futurama. Original airdate June 1, 2003. No. 12, Season 4. 20th Century Fox.
- ^ a b Cohen, David X (2003). Futurama season 1 DVD commentary for the episode "Space Pilot 3000" (DVD). 20th Century Fox.
- ^ "I Dated a Robot". Futurama. Fox Network. 2001-05-13. No. 15, season 3.
- ^ "Proposition ∞". Futurama. Fox Network. 2010-07-08. No. 4, season 6.
- ^ a b Pinsky, Mark (2003). The Gospel According to the Simpsons. Bigger and possibly even Better! edition. pp. 229–235. ISBN 978-0-664-23265-8.
- ^ "Love's Labours Lost in Space". Futurama. Fox Network. 1999-04-13. No. 4, season 1.
- ^ a b Azrai, Ahmad (2004-10-31). "Farewell to the funny future". Asia Africa Intelligence Wire. http://www.accessmylibrary.com/coms2/summary_0286-14221036_ITM. Retrieved 2008-01-10.
- ^ "'Flickr Slideshow'". http://www.flickr.com/photos/nachop/sets/450093/show/. Retrieved 2007.
- ^ Cohen, David X.; Groening, Matt; Kelley, Brian; Sheesley, Brian; Moore, Rich; Vanzo, Scott; DiMaggio, John (2002). Futurama: Volume One DVD commentary for the episode "Love's Labours Lost in Space" (DVD). 20th Century Fox. "Scott Vanzo: The final is kinda difficult for us to create, it has over 80 levels of 3D animation that are composited together, a lot of cheats, probably the single biggest scene that we have ever done, or at least we view it as a scene, so... I don't know what else to say. David X. Cohen: How long did it take just to animate that 28 seconds? Vanzo: I think we did it in about four or five weeks, all together."
- ^ Cohen, David X.; Groening, Matt; Kelley, Brian; Sheesley, Brian; Moore, Rich; Vanzo, Scott; DiMaggio, John (2002). Futurama: Volume One DVD commentary for the episode "Love's Labours Lost in Space" (DVD). 20th Century Fox. "David X. Cohen: How long does it take — out of curiosity, I don't even the answer to this — how long does it take to render one frame of that kind of degree of computer– 3D computer graphics? Scott Vanzo: We split it into a lot of different levels, because it was taking so long, and that way we can fix things a lot easier. I would say, probably about an hour a frame for that title. Cohen: And 30 frames per second? So that adds up."
- ^ "Omniglot". http://www.omniglot.com/writing/futurama.htm. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ "The Day the Earth Stood Stupid". Futurama. Audio Commentary 11 minutes in.
- ^ "Space Pilot 3000". Futurama. Fox Network. 1999-03-28. No. 01, season 1. Audio commentary 20 minutes in.
- ^ Keller, Joel (January 31, 2007). Matt Groening talks about Futurama's comeback. TV Squad. Retrieved February 1, 2007.
- ^ a b "Raging Bender". Futurama. Fox Network. 2000-02-27. No. 8, season 2.
- ^ "The Luck of the Fryrish". Futurama. Fox Network. 2001-03-11. No. 4, season 3.
- ^ "The 30% Iron Chef". Futurama. Fox Network. 2002-04-14. No. 22, season 3.
- ^ "Put Your Head on My Shoulders". Futurama. Fox Network. 2000-02-13. No. 7, season 2.
- ^ "Fry and the Slurm Factory". Futurama. Fox Network. 1999-11-14. No. 13, season 1.
- ^ "Teenage Mutant Leela's Hurdles". Futurama. Fox Network. 2003-03-30. No. 9, season 4.
- ^ "Fear of a Bot Planet". Futurama. Fox Network. 1999-04-20. No. 5, season 1.
- ^ "Put Your Head On My Shoulders". Futurama. Fox Network. 1999-04-20. No. 10, season 2.
- ^ Booker, M. Keith. Drawn to Television: Prime-Time Animation from The Flintstones to Family Guy. pp. 115–124.
- ^ Bauder, David (1999-04-01). "New animated show `Futurama' may be a score for Fox". The Milwaukee Journal Sentinel. http://nl.newsbank.com/nl-search/we/Archives?p_product=MWSB&p_theme=mwsb&p_action=search&p_maxdocs=200&p_topdoc=1&p_text_direct-0=0EB82C9405B7CAA1&p_field_direct-0=document_id. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ "Groening's Gripe". April 1999. http://web.archive.org/web/20000824051808/www.frcr.com/library/dailytv1.html. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ Sterngold, James (1999-07-22). "Futurama: Bringing an Alien and a Robot to TV Life". New York Times. http://web.archive.org/web/20000824051735/www.frcr.com/library/new_york_times1.html. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ "Fox puts 'Futurama' order on hold". 2002-02-14. http://www.medialifemagazine.com/news2002/feb02/feb11/4_thurs/news7thursday.html. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ a b "Toon Net Gets 'Futurama'". Daily Variety. September 9, 2002. http://www.accessmylibrary.com/coms2/summary_0286-26075307_ITM. Retrieved 2008-05-28.
- ^ Dempsey, John (October 27, 2005). ""Futurama" in Comedy Central's future via big deal". Variety. http://www.variety.com/article/VR1117931802.html?categoryid=14&cs=1. Retrieved 2005-10-27.
- ^ "Silver screen Simpsons, Futurama facing finish?". BBC News. 2001-01-19. Archived from the original on 2003-04-19. http://web.archive.org/web/20030419181300/http://www.bbc.co.uk/cult/news/02021902.shtml. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ a b Gorman, Bill (June 25, 2010). "UPDATED Thursday Cable Ratings: Futurama Returns Strong; Plus Burn Notice, Royal Pains, NBA Draft & More". http://tvbythenumbers.com/2010/06/25/thursday-cable-ratings-futurama-returns-strong/55378?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+Tvbythenumbers+%28TVbytheNumbers%29. Retrieved 2010-06-26.
- ^ a b "Awards for "Futurama" (1999)". http://www.imdb.com/title/tt0149460/awards. Retrieved 2006-06-12.
- ^ "29th Annual Annie Award Nominees and Winners". Archived from the original on 2005-03-12. http://web.archive.org/web/20050312140353/http://www.annieawards.com/29thannieawardwinners.htm.
- ^ "Primetime Emmy Awards nominations for 2011 - Outstanding Animated Program". http://www.emmys.com/nominations/2011/Outstanding%20Animated%20Program.
- ^ "Primetime Emmy Awards nominations for 2011 - Outstanding Voice-Over Performance". http://www.emmys.com/nominations/2011/Outstanding%20Voice-Over%20Performance.
- ^ "Futurama nominated for 2 Annie Awards 2011". Slurmed.com. 2010-12-07. http://slurmed.com/news/2010-12-07/futurama-nominated-for-2-annie-awards-2011. Retrieved 2011-08-23.
- ^ "Top 100 Animated TV Series". IGN. January 2009. http://tv.ign.com/top-100-animated-tv-series/8.html. Retrieved 22 March 2010.
- ^ "Groening lanches 'Futurama Comics'". 2000-11-19. http://nl.newsbank.com/nl-search/we/Archives?p_product=NewsLibrary&p_multi=CSGB&d_place=CSGB&p_theme=newslibrary2&p_action=search&p_maxdocs=200&p_topdoc=1&p_text_direct-0=0F34B832C954DA1A&p_field_direct-0=document_id&p_perpage=10&p_sort=YMD_date:D&s_trackval=GooglePM. Retrieved 2007-07-16.
- ^ Press release (2002-09-25) Do you want Fry with that? Titan Publishing. Retrieved from gotfuturama on 2007-03-04
- ^ Rabin, Nathan (2006-04-26). "Matt Groening". The A.V. Club. http://www.avclub.com/articles/matt-groening,13984/. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ "Rhymes with Raining". Crave Online. 2007-02-26. http://www.craveonline.com/articles/filmtv/04647510/rhymes_with_raining.html. Retrieved 2007-03-25.
- ^ "Ain't It Cool News: "Ben Sinister Has Read The New FUTURAMA 'Movie'!!"". http://www.aintitcool.com/display.cgi?id=24076. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ (April 5, 2008). Tales of Interest: The Simpsons and Futurama in high-definition. HDTVTotal.com.
- ^ ""Futurama" Feature Length Movie DVD Specs". 2007-11-14. http://www.2snaps.tv/9812689. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ Hornig, Andreas (2008-07-28). "Futurama's third direct-to-disc movie "Bender's Game" on Blu-ray". HDTVTotal.com. http://www.hdtvtotal.com/module-pagesetter-viewpub-tid-1-pid-1210.html. Retrieved 2008-08-10.
- ^ "Into the Wild Green Yonder at Blu-ray.com". Blu-ray.com. http://www.blu-ray.com/movies/movies.php?id=1889. Retrieved 2009-02-23.
- ^ "Futurama Finds a Developer". http://www.gamespot.com/news/2628824.html?q=Futurama. Retrieved 2006-07-25.
- ^ "Sierra to bring Futurama game to the US". http://www.gamespot.com/news/6025618.html?q=Futurama. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ "Futurama Info — Futurama Information — Futurama Release Date". http://www.gamefaqs.com/console/gamecube/data/583447.html. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ http://www.comedycentral.com/shows/futurama/index.jhtml
- ^ http://sky1.sky.com/sky1hd-shows
- ^ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Teletoon_at_Night#Current_programs
- ^ Janulewicz, Tom (2000-02-29). "Pushing Tin: Space Toys With Golden-Age Style". http://www.space.com/sciencefiction/toyfair_tinworks_000229.html. Retrieved 2007-07-16.
- ^ Huxter, Sean (2001-03-05). "Bender: Matt Groening's Futurama inspires a nostalgia for the inventive toys of future past". Archived from the original on October 11, 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20071011135728/http://www.scifi.com/sfw/cool/sfw6707.html. Retrieved 2007-07-16.
- ^ "Futurama SDCC Exclusive and Toy news". Archived from the original on September 29, 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20070929034559/http://www.action-figure.com/index.php?name=News&file=article&sid=19970. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
External links
- Official website
- Futurama at the Internet Movie Database
- Futurama at TV.com
- The Infosphere — a Futurama wiki
- The Futurama Wiki at Wikia
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||